Underwater Image Enhancement via a Robust yet Efficient Dual Prior Optimized Method
Top Reasons to Join SPS Today!
1. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine
2. Signal Processing Digital Library*
3. Inside Signal Processing Newsletter
4. SPS Resource Center
5. Career advancement & recognition
6. Discounts on conferences and publications
7. Professional networking
8. Communities for students, young professionals, and women
9. Volunteer opportunities
10. Coming soon! PDH/CEU credits
Click here to learn more.
Underwater Image Enhancement via a Robust yet Efficient Dual Prior Optimized Method
Contributed by Dr. Weidong Zhang, based on the IEEEXplore® article, “Underwater Image Enhancement via Piecewise Color Correction and Dual Prior Optimized Contrast Enhancement”, published in the IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023.
Introduction
Underwater images are highly susceptible to quality degradation due to light's scattering and absorption [1,2]. Unfortunately, underwater images with deteriorating quality impose many limitations in following visual perception analysis and practical underwater applications, such as trepang detection, driver detection, marine organism grab [3,4], etc. As a result, improving underwater image quality positively affects underwater vision applications.
Currently, the techniques to solve the degradation of underwater image quality mainly include non-model-driven, model-driven, and data-driven methods [5,6]. Non-model-driven methods rely on adjusting the pixel value of an image to improve the quality of the image. Its representative methods include Retinex-based, histogram-based, and fusion-based methods. Model-driven methods solve the imaging model parameters using priors to restore high visibility images. Its representative priors include minimum information loss prior, scene depth prior, statistical prior, sparse prior, etc. Recently, data-driven methods using GAN or GNN models have been successfully applied to underwater image enhancement thanks to large-scale training data [7]. However, high quality training data restrict the effectiveness and robustness of deep learning methods.
To advance the development of underwater image enhancement, we propose a Piecewise Color Correction and Dual Prior Optimized Contrast Enhancement, called PCDE. Specifically, we first present the piecewise color correction method using the maximum mean and two gain factors to correct the color cast of each color channel. Then, we propose a dual prior optimized contrast enhancement method, which relies on the spatial and texture priors to decompose the base layer and detail layer of the V channel in HSV color space. Meanwhile, we employ different enhancement strategies in different layers to enhance the contrast and texture detail of underwater images. Fig. 1 presents our PCDE enhanced results for several raw images with degraded quality. Without fine-tuning the parameters, PCDE consistently yields visually pleasing results, benefiting from our designs.
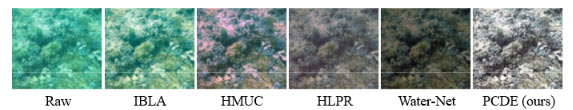
Figure 1: Samples of our enhanced results. From left to right are the results of different methods of enhancement.
The Proposed Method
In this work, the underwater image enhancement in Fig. 2, includes two main stages: color correction and contrast enhancement. First, a segmented color correction method is introduced, which corrects color deviations in each channel using the maximum mean and two gain factors. Then, in the HSV color space, the V channel is decomposed, where a spatial prior is constructed to optimize and enhance the base layer, and a texture prior is used to refine and sharpen the detail layer. Different enhancement strategies are applied to improve contrast and texture details accordingly.
The proposed PCDE is different from existing methods. We emphasize the contributions of this work as follows.
- We propose a piecewise color correction method, which first employs the maximum mean value to divide each color channel into two pieces. Whereafter, a piecewise color correction strategy with two gain factors adaptively corrects the color cast of each color channel.
- We design a dual prior optimized contrast enhancement strategy to improve the quality of the color-corrected image, in which the spatial prior is designed to optimize and enhance the base layer of the image, and the texture prior is used to optimize and sharpen the detail layer of the image.

Figure 2: Flowchart of the proposed method.
Piecewise Color Correction
To effectively cope with the traditional linear transmission methods for color correction prone to introducing the red cast and local artifacts, we propose a piecewise linear transmission method for color correction. We first calculate the average gray value of each color channel, and then use the maximum gray mean value as a reference value to calibrate each color channel to obtain a color corrected image.
Dual Prior Optimized Contrast Enhancement
Besides color correction, we propose a contrast enhancement method based on dual-layer decomposition optimization, utilizing spatial and texture priors to optimize the input image in a layered manner, thereby improving overall contrast and detail clarity. First, the input image is decomposed into two layers: a base layer and a detail layer. Then, gradient operations and norm optimization are employed to compute the decomposition parameters, and local mean-based adaptive adjustment is applied to different brightness regions to enhance dark details while preventing overexposure in bright areas. For the detail layer, a detail stretching method is used to enhance weak edges and texture information, making them more prominent. Meanwhile, the degree of detail enhancement is adaptively adjusted based on local contrast distribution to prevent noise amplification or edge artifacts. Finally, an edge enhancement strategy is adopted to highlight key structural information, making object contours clearer, thereby significantly improving the visual quality and recognizability of underwater images.
Experimental Results
To demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, we test our method on UCCS, UIQS, and UIEB as shown in Fig. 3. Our method has surpassed popular image enhancement methods. In comparison, our method effectively removes unnatural colors and improves visibility without obvious over-enhancement, under-enhancement, and local darkness.
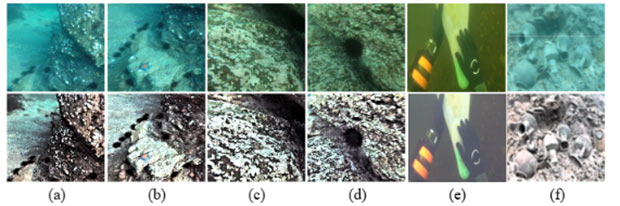
Figure 3: Samples of our enhanced results (bottom) for diverse raw underwater images (top). Raw underwater images in (a) and (b) are sampled from UCCS. Raw underwater images in (c) and (d) are sampled from the UIQS. Raw underwater images in (e) and (f) are sampled from the UIEB. Without fine-tuning the parameters, our method consistently yields visually pleasing results.
References:
[1] W. Zhang, P. Zhuang, H. -H. Sun, G. Li, S. Kwong and C. Li, "Underwater Image Enhancement via Minimal Color Loss and Locally Adaptive Contrast Enhancement," in IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 31, pp. 3997-4010, 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3177129
[2] P. Zhuang, J. Wu, F. Porikli and C. Li, "Underwater Image Enhancement With Hyper-Laplacian Reflectance Priors," in IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 31, pp. 5442-5455, 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3196546
[3] W. Zhang et al., "Underwater Image Enhancement via Weighted Wavelet Visual Perception Fusion," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 2469-2483, 2023, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3299314
[4] C. Li et al., "An Underwater Image Enhancement Benchmark Dataset and Beyond," in IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 29, pp. 4376-4389, 2020, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2955241.
[5] W. Zhang, Q. Liu, Y. Feng, L. Cai and P. Zhuang, "Underwater Image Enhancement via Principal Component Fusion of Foreground and Background," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 34, no. 11, pp. 10930-10943,2024, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3412748
[6] W. Zhang, Q. Liu, H. Lu, J. Wang and J. Liang, "Underwater Image Enhancement via Wavelet Decomposition Fusion of Advantage Contrast," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2025.3545595
[7] C. Li, S. Anwar, J. Hou, R. Cong, C. Guo and W. Ren, "Underwater Image Enhancement via Medium Transmission-Guided Multi-Color Space Embedding," in IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 30, pp. 4985-5000, 2021,DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3076367
SPS Social Media
- IEEE SPS Facebook Page https://www.facebook.com/ieeeSPS
- IEEE SPS X Page https://x.com/IEEEsps
- IEEE SPS Instagram Page https://www.instagram.com/ieeesps/?hl=en
- IEEE SPS LinkedIn Page https://www.linkedin.com/company/ieeesps/
- IEEE SPS YouTube Channel https://www.youtube.com/ieeeSPS











