SPS Blog Post: An Echo in Time: Tracing the Evolution of Beamforming Algorithms
SPS Blog Post: August 2023
Contributed by Ahmet M. Elbir, Kumar Vijay Mishra, Sergiy A. Vorobyov and Robert W. Heath, Jr., based on the IEEEXplore® article, “Twenty-Five Years of Advances in Beamforming: From convex and nonconvex optimization to learning techniques,” published in the 75th Anniversary Edition of the IEEE Signal Processing Magazine in June 2023, and the 75th Anniversary Webinar with the same title, available on the SPS Resource Center.
Introduction
Beamforming is a widely used signal processing technique that exploits arrays of sensors improve one of many possible application-driven performance objectives [1]. It finds applications in several engineering applications such as radar, sonar, wireless communications, acoustics, astronomy, seismology, and medical imaging. Recent advances in mobile communications, usage of large arrays, high-frequency sensors, near-field signal recovery, and smart radio environments have opened interesting and novel signal processing problems in beamforming (Fig. 1). This post summarizes the evolution of beamforming algorithms as encapsulated in our recent article “Twenty-Five Years of Advances in Beamforming: From convex and nonconvex optimization to learning techniques” published in the IEEE Signal Processing Magazine.
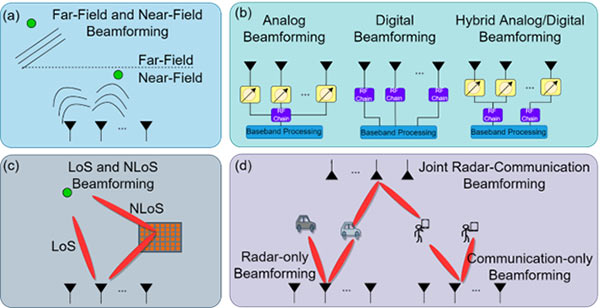
Figure 1. Major classes of beamforming techniques by (a) transmission range: far and near fields; (b) transceiver architectures: analog, digital, and hybrid beamforming; (c) paths: line-of-sight (LoS) and and non-LoS (NLoS) beamforming, wherein the NLoS path is controlled via joint active (transmitter) and passive (intelligent reflecting surface) devices; (d) applications: radar, communications, and joint radar-communications.

